Home > Publications
Srivastava AP, Luo M, Zhou W, Symersky J, Bai D, Chambers MG, Faraldo-Gómez JD, Liao M, Mueller DM
doi: 10.1126/science.aas9699
Srivastava AP, Luo M, Zhou W, Symersky J, Bai D, Chambers MG, Faraldo-Gómez JD, Liao M, Mueller DM. High-resolution cryo-EM analysis of the yeast ATP synthase in a lipid membrane. Science. 2018 May 11;360(6389):eaas9699. doi: 10.1126/science.aas9699. Epub 2018 Apr 12. PMID: 29650704; PMCID: PMC5948177.
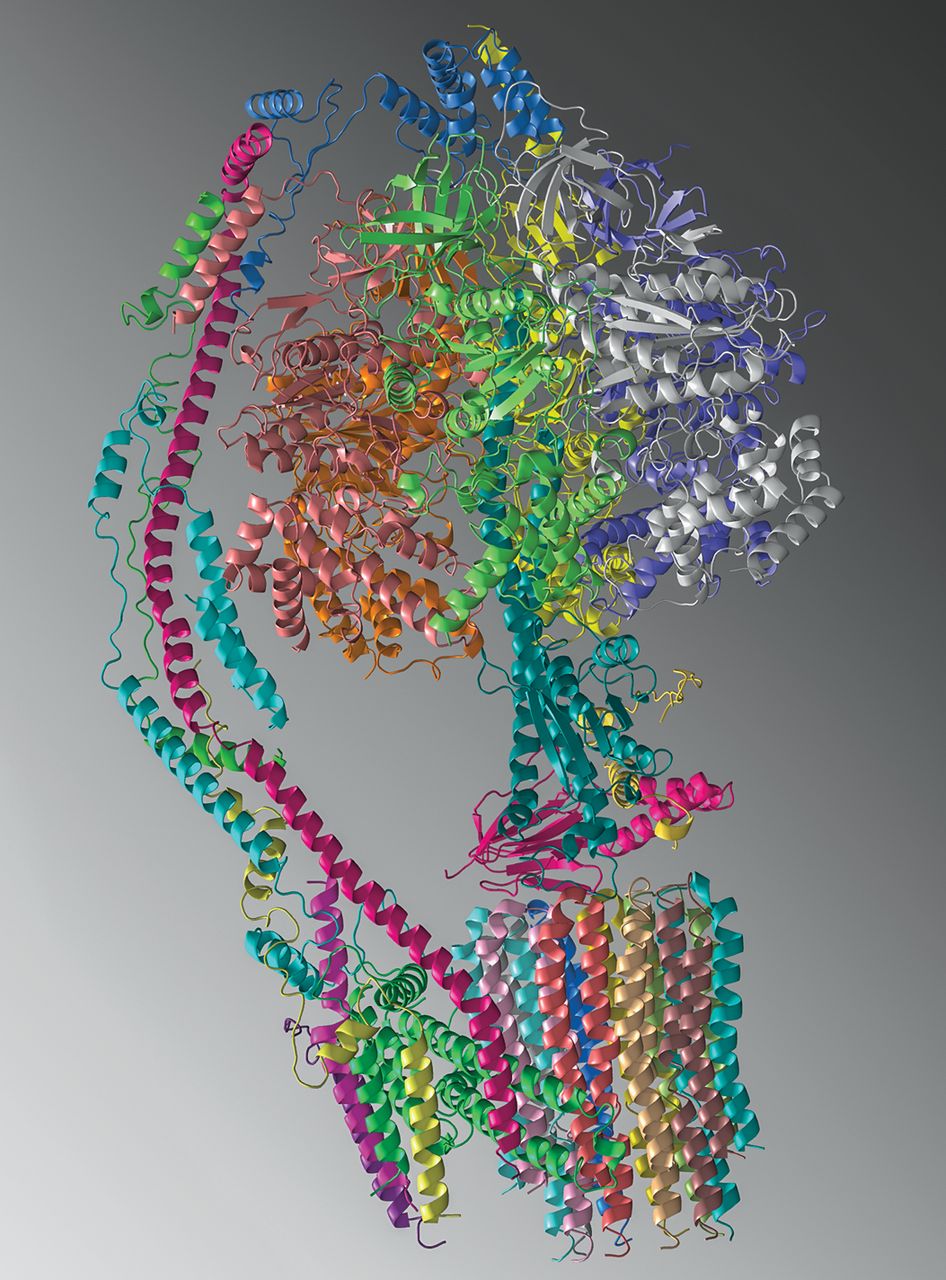
Mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase comprises a membrane embedded Fo motor that rotates to drive ATP synthesis in the F1 subunit. We used single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to obtain structures of the full complex in a lipid bilayer in the absence or presence of the inhibitor oligomycin at 3.6- and 3.8-angstrom resolution, respectively. To limit conformational heterogeneity, we locked the rotor in a single conformation by fusing the F6 subunit of the stator with the δ subunit of the rotor. Assembly of the enzyme with the F6-δ fusion caused a twisting of the rotor and a 9° rotation of the Fo c10-ring in the direction of ATP synthesis, relative to the structure of isolated Fo Our cryo-EM structures show how F1 and Fo are coupled, give insight into the proton translocation pathway, and show how oligomycin blocks ATP synthesis.